The Post-Quantum Cryptography transition has evolved past a compliance checklist to a structural stress test. Architects have shifted past debating the selection of algorithms. They now confront the physical wall limits of legacy silicon and network stacks.
Mitech Punto performed a data-driven audit of the 2026 cryptography landscape. The purpose of this report is to highlight the impedance that 20th-century infrastructure imposes on 21st-century math. This text connects the threat level and the technical remediations needed to avert systemic failures.
The 2026 Post-Quantum Cryptography Strategic Pivot: Executive Summary
The 2026 lattice-based cryptography mandates represent a fundamental collision between legacy infrastructure and its physical requirements. This audit identifies that the primary enterprise risk is more than theoretical algorithmic breakage. It involves the immediate threat of hardware saturation and network lockout.
Infrastructure that cannot natively process the expanded payload of quantum-safe handshakes is effectively a depreciating liability. For the architect, the priority must shift from “cryptographic agility” as a software concept to “structural integrity” as a physical requirement.
Failure to address the impedance mismatch in the transport layer and the silicon logic will result in deterministic outages. It also causes a catastrophic loss of throughput. Classical systems will reach a terminal breaking point under the weight of PQC math without specific structural remediation.
- Network Decoupling: The 2026 transition requires moving fragmentation logic out of the network layer and into the cryptographic stack to prevent firewalls from dropping 3.3KB payloads.
- Hardware Amortization: General-purpose HSMs have reached a terminal compute ceiling. Future-proofing infrastructure requires a transition to matrix-accelerated silicon to maintain wire-speed.
- Identity Integrity: Maintaining Zero Trust at scale necessitates the adoption of high-efficiency signatures, like FN-DSA, to prevent the systemic latency inherent in standard ML-DSA deployments.
| Algorithm Family (NIST Standard) | Public Key Size (Post-Quantum) | Signature / Ciphertext Payload | Structural Significance: Network & Physics | 2026 FIPS Compliance Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classical (RSA-3072) | 384 Bytes | 384 Bytes | Baseline Efficiency: Handshakes fit within a single 1,500B Ethernet frame. No fragmentation. | CNSA 2.0 Deprecation Roadmap |
| Classical (ECDSA P-256) | 64 Bytes | 64 Bytes | Zero Overhead: Optimized for IoT and mobile. Fits within standard TCP/UDP segments. | CNSA 1.0 Deprecation Phase |
| PQC (ML-KEM-768) | 1,184 Bytes | 1,088 Bytes | The First Wall: Approaches 1,500B MTU limit. Adds ~3KB to TLS 1.3 handshakes. | FIPS 203 Mandatory |
| PQC (ML-DSA-65) | 1,952 Bytes | 3,309 Bytes | Fragmentation Trigger: Exceeds MTU. Triggers IP-layer fragmentation in legacy firewalls. | FIPS 204 Mandatory |
| PQC (FN-DSA-512) | 897 Bytes | 666 Bytes | Identity Target: 80% smaller signatures than ML-DSA. Ideal for machine identity. | FIPS 206 Mandatory |
1. The Packet Fragmentation Bottleneck
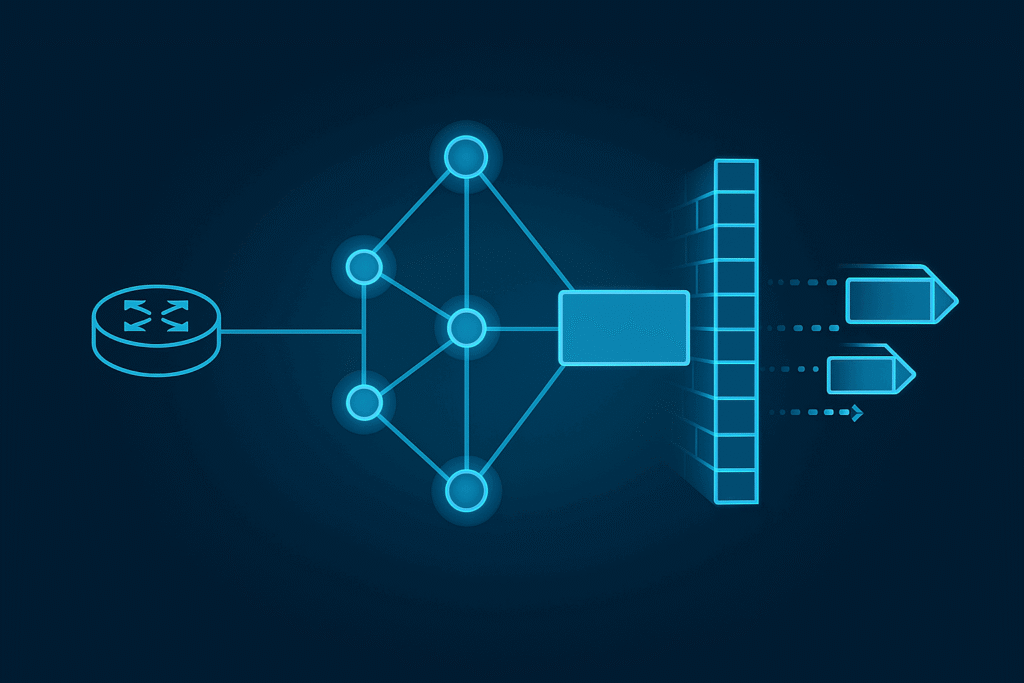
Integrating NIST-standardized algorithms, such as ML-KEM-768 and ML-DSA-65, introduces a fundamental payload conflict. Classical ECDH P-256 keys are 32 bytes, while ML-KEM-768 public keys are 1,184 bytes, and ML-DSA-65 signatures reach 3,309 bytes.
This asymmetry causes the network to fragment cryptographic handshakes across multiple frames. That is because they significantly exceed the standard 1,500-byte MTU.
Why Do PQC Handshakes Trigger Systemic Drops in High-Security Firewalls?
Structural audits of legacy networking equipment confirm that a handshake that exceeds the MTU gets fragmented at the IP layer. In production, firewalls, load balancers, and DDoS scrubbers are the high-security middleboxes. These often misidentify these fragmented handshakes as malformed packet attacks or state-exhaustion floods.
The connection drop is not because of a breach. It happens because security hardware is configured to discard highly fragmented traffic by default. This aims to prevent buffer-exhaustion attacks and state-table overflows during the extended reassembly window required by lattice-based payloads.
This creates a “silent outage” where PQC-enabled clients fail to connect through legacy gateways.
Does the Current Network Topology Support the 3.3KB Payload Threshold Required by FIPS 204?
Architects must abandon IP-level fragmentation to resolve this incompatibility. Our data modeling concludes that RFC 9370 (Multiple Key Exchanges) complements the IKEv2 fragmentation (RFC 7383) to stabilize hybrid VPNs.
Moving the fragmentation logic into the cryptographic stack ensures the system can break down payloads before they hit the network layer. This ensures firewalls receive standard, right-sized, encrypted frames instead of triggering security drops on fragmented anomalies.
Adopting a 9,000-byte Jumbo Frame MTU for internal East-West traffic represents the only definitive method for stripping away reassembly overhead. This architectural move directly reclaims the 15–20% latency tax identified in current benchmarks. It transforms a structural bottleneck into wire-speed performance.
2. Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD) and Black Holes
The network structure stability in the post-quantum regime greatly depends on the network’s ability to transmit the constraints of paths effectively. Standard methods fail in the discovery phase as large payloads of PQC facilitate deterministic timeouts of connections.
How Does Path MTU Discovery Failure Break Quantum-Safe VPN Tunnels?
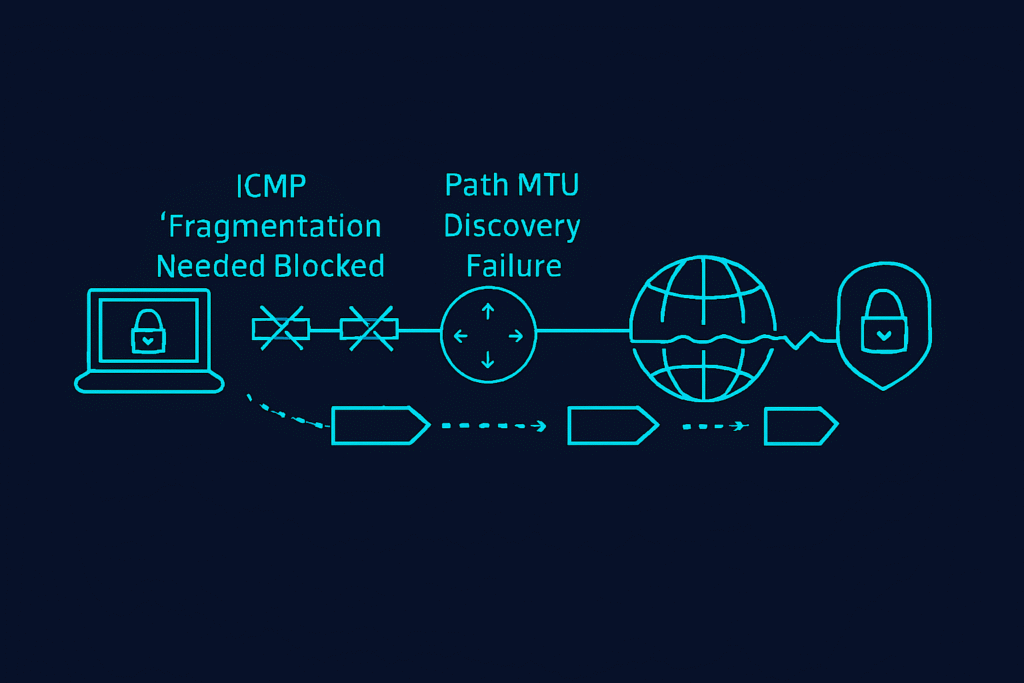
Audit findings suggest that many of the VPN appliances and cellular NAT gateways have strict policies that discard fragmented UDP traffic. Comparative analysis of tunnel stability has confirmed that in cases where infrastructure does not support protocol-level fragmentation, the handshake simply never completes.
This is exacerbated by the use of ICMP black holing. The PMTUD messages are dropped, and the sender remains unaware that their 3,309-byte PQC signature is being discarded at a mid-path hop.
What Is the Capex Exposure for Remediating ICMP Black Holing Across Legacy Edge-Nodes?
The problem requires a two-fold change in the transport layer. The first change involves setting up TCP MSS Clamping at 1,200 bytes. The configuration ensures enough headroom for the 1,184-byte ML-KEM-768 public key to be contained in one 1,500-byte MTU. This bypasses the fragmentation hurdles present in legacy middleboxes.
In UDP-intensive protocols, such as QUIC, the audit mandates enforcing Datagram Path MTU Discovery (DPLPMTUD) compliance. This active probing of path capacity is the only deterministic defense against the “silent black hole” effect. It ensures the network dynamically adjusts to the payload weight of hybrid PQC deployments.
3. The Machine Identity Recursive Loophole
Structural failures in Identity and Access Management (IAM) have surfaced as the 2026 requirement for Agentic Autonomy clashes with the PQC transition. This proliferation of autonomous agents spawning sub-agents for micro-tasks builds a web of delegated authority that legacy frameworks lack the capacity to contain.
How Does Recursive Delegation Forge Over-Privileged Attack Surfaces Within Agentic Chains?
Structural audits of multi-agent ecosystems reveal that traditional identity systems are built for static service accounts and fail to secure multi-entity delegations. In 2026-era deployments, sub-agents often inherit the full root-level credentials of the parent.
That happens because the infrastructure cannot handle generating unique, PQC-signed identities for every ephemeral micro-operation. It is a compute-heavy task. This creates a liability where a compromised leaf agent, like performing a task as simple as data retrieval, provides an adversary with the fiduciary power of the entire lineage.
Is FN-DSA the Only Viable Path to Maintaining Sub-Second Zero Trust Validation?
Zero Trust architecture collapses when machine identities lack cryptographic agility. When an agent’s signature is rooted in classical ECC, it becomes vulnerable to ‘Harvest Now, Decrypt Later’ exploitation. However, the shift to NIST standards, like ML-DSA-65, elevates identity payloads from 64 bytes to 3,309 bytes per signature.
Architectural reviews confirm that this 50x signature bloat increase often leads developers to bypass security checks for internal agent-to-agent communication. This creates a dangerous dissonance where a ‘Zero Trust’ policy on paper is physically enforced as ‘Implicit Trust’ because the PQC overhead is too high to sustain at scale.
To bridge this gap, the audit identifies that the strategic alternative for ephemeral identity is FN-DSA. The ML-DSA is the NIST standard for general use. FN-DSA provides signatures of 666 bytes. It is 80% smaller and speeds up verification. A switch to FN-DSA in the internal identity fabric will enable PQC fully and eliminate the latency peaks that usually cause the developer to turn off security verification in the high-speed internal environment.
4. The Hybrid-Handshake Performance Tax
Bridging the gap between classical and quantum-safe math in the 2026-forward industry requires Hybrid Cryptography. Running RSA or ECC alongside ML-KEM provides a safety net against algorithmic breakage. However, this imposes a compute ceiling that legacy data centers cannot support without significant latency penalties.
Why Does Dual-Algorithm Processing Push Current HSMs to a 90% CPU Failure State?
Data-driven benchmarks of FIPS 140-3 validated Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) confirm that running two concurrent cryptographic protocols is an exponential drain on resources. Current modules hit saturation during the handshake phase alone, leaving zero headroom for actual data processing.
This is the CapEx Cliff. Architectural modeling indicates that a hybrid handshake peaks CPU utilization at 92% when it receives 500 new handshakes per second (TPS). It is a workload legacy ECC handled at 15%.
What Is the ROI on Matrix-Accelerated Silicon vs. General-Purpose CPUs?
![]()
The solution is a shift in silicon architecture. Legacy modules rely on general-purpose processors. These struggle with the polynomial ring multiplication central to lattice-based math. Future-proofed infrastructure requires Matrix-Accelerated HSMs, such as the NVIDIA Blackwell B300.
These units can handle PQC handshakes as vectorized workloads. They allow the system to maintain wire-speed throughput and free up the main CPU for application logic.
Engineering durability also necessitates Session Resumption Optimization. Implement aggressive TLS Session Resumption via session tickets at the load balancer and edge. It ensures the resource-intensive PQC handshake occurs only once. This configuration establishes a long-lived session key that effectively amortizes the latency tax across thousands of transactions.
5. Stranded Capital: The Balance Sheet Collision
The PQC pivot introduces a write-down event for enterprise infrastructure. From an architect’s lens, signature bloat is a bottleneck. And it is Asset Impairment from a director’s view.
Legacy HSMs are no longer assets once they reach saturation. They become liabilities that threaten business continuity. Organizations holding long-term intellectual property face “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” risks. This represents a silent erosion of intangible assets and terminal valuation.
| Architectural Pillar | Technical Friction & Collision | 2026 Regulatory Milestone | Engineering Remediation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transport Layer | Payload Conflict: 3.3KB ML-DSA payload causes VPN tunnel drops due to ICMP black-holing. | CNSA 2.0 VPN Deadline | Implement RFC 9370 (Multiple KEMs) and force MSS Clamping at 1,200B. |
| Silicon Logic | Compute Ceiling: Hybrid handshakes (RSA + PQC) push legacy HSM CPUs to 92% saturation. | FIPS 140-3 Transition | Replace general-purpose HSMs with Matrix-Accelerated Silicon (NVIDIA B300). |
| Identity Fabric | Recursive Tax: Agentic autonomy spawns 100+ sub-agents, each requiring unique 3KB PQC IDs. | EO 14028 Mandates | Transition internal service mesh to FN-DSA to reduce verification latency. |
How Does the 2026 Mandate for Engineering Durability Affect Legacy Network Architecture?
On the balance sheet, an architecture unable to handle a 3,309-byte signature or a recursive machine identity is a legacy liability. Structural integrity in the post-quantum era requires a shift from policy-based audits to a physical assessment of infrastructure capacity.
Engineering durability depends on the hardware’s ability to process lattice-based mathematics without deterministic failure or systemic latency.
Institutional Disclosure: This analysis is pure architectural auditing and technical intelligence. It does not constitute legal, regulatory, or investment counsel. Engineering requirements and deployment mandates are subject to NIST and CISA revision cycles.